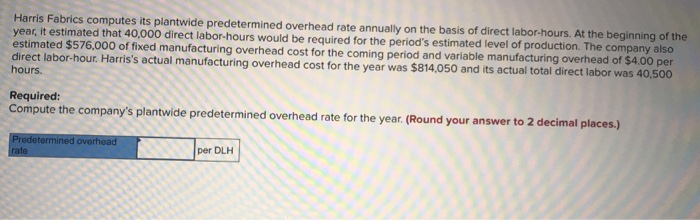
Harris fabrics computes its plantwide – In the realm of cost accounting, Harris Fabrics stands out for its meticulous approach to plantwide computation. This practice involves meticulously allocating overhead costs across all production activities, enabling the company to make informed decisions and optimize its operations.
Harris Fabrics’ plantwide computation journey offers valuable insights into the complexities of cost allocation. By examining their methods, techniques, and the factors influencing their overhead rates, we can gain a deeper understanding of how accurate cost allocation can drive better decision-making.
Plantwide Computation Overview
Plantwide computation is a method of allocating indirect costs to products or services based on a single plantwide rate. This rate is calculated by dividing the total indirect costs by the total direct labor hours or other appropriate allocation base.
Plantwide computation is a simple and straightforward method that is often used by small businesses.
Benefits of Plantwide Computation
- Simplicity: Plantwide computation is a simple and straightforward method that is easy to understand and implement.
- Low cost: Plantwide computation is a relatively low-cost method to implement and maintain.
- Accuracy: Plantwide computation can be a relatively accurate method of allocating indirect costs, especially for small businesses with a limited number of products or services.
Limitations of Plantwide Computation
- Inaccuracy: Plantwide computation can be inaccurate for businesses with a diverse range of products or services, as it does not take into account the different costs associated with each product or service.
- Complexity: Plantwide computation can become complex for businesses with a large number of products or services, as it requires the calculation of a separate plantwide rate for each product or service.
Methods and Techniques
Harris Fabrics employs various methods and techniques to compute plantwide overhead rates. These methods involve selecting appropriate allocation bases and applying them to different overhead cost pools.
The choice of allocation base is crucial as it determines how overhead costs are assigned to different cost objects (e.g., products or departments). Common allocation bases include:
Direct Labor Hours
- Direct labor hours represent the time spent by workers directly involved in production.
- Using direct labor hours as an allocation base assumes that overhead costs are incurred in proportion to the amount of labor required to produce a unit.
Machine Hours
- Machine hours measure the time that machines are used in production.
- This allocation base is suitable when overhead costs are primarily related to the operation of machinery, such as depreciation, maintenance, and utilities.
Units Produced
- Units produced represent the number of units manufactured during a period.
- Using units produced as an allocation base assumes that overhead costs are incurred uniformly across all units produced.
Factors Affecting Plantwide Rates
Harris Fabrics’ plantwide overhead rates are influenced by a combination of factors, including production volume, activity levels, and resource utilization. Understanding these factors is crucial for accurate cost allocation and effective decision-making.
Volume-Related Factors
Volume-related factors directly impact the plantwide overhead rate. Higher production volumes lead to lower overhead rates as fixed costs are spread across a larger number of units. Conversely, lower production volumes result in higher overhead rates due to the underutilization of resources.
Activity-Based Factors
Activity-based factors measure the level of activity within the plant. Changes in activity levels, such as increased machine hours or labor hours, can affect the overhead rate. Higher activity levels lead to lower overhead rates as fixed costs are absorbed by a greater number of activities.
Resource Utilization
Resource utilization refers to the efficiency with which resources are used. Poor resource utilization, such as idle time or inefficient processes, can lead to higher overhead rates. Conversely, effective resource utilization results in lower overhead rates as resources are used productively.
Impact on Decision-Making
Harris Fabrics utilizes plantwide overhead rates in its decision-making processes to ensure accurate and informed choices regarding resource allocation and production planning.
Accurate plantwide rates provide a comprehensive view of the true cost of production, enabling Harris Fabrics to make informed decisions about product pricing, production levels, and resource allocation.
Decision-Making Examples
For instance, accurate plantwide rates can assist in determining the appropriate selling price for products. By accurately capturing all manufacturing costs, Harris Fabrics can set prices that cover both direct and indirect expenses, ensuring profitability.
Additionally, accurate plantwide rates aid in production planning. Harris Fabrics can optimize production schedules by understanding the total cost of producing different products. This knowledge enables them to prioritize high-margin products and allocate resources efficiently.
Case Study or Real-World Example
Harris Fabrics, a textile manufacturing company, implemented plantwide computation to allocate overhead costs to its various departments. The company had previously used a traditional departmental allocation method, which resulted in inequitable cost allocation and inaccurate product costing.
Harris Fabrics conducted a thorough analysis of its manufacturing process and identified several cost pools that were shared by multiple departments. These cost pools included rent, utilities, and equipment maintenance. The company then selected a single plantwide overhead rate based on the total cost of these shared cost pools divided by the total units of production.
Benefits of Plantwide Computation
- Improved cost allocation accuracy: Plantwide computation ensured that overhead costs were allocated more fairly to each department, regardless of its size or activity level.
- Simplified cost accounting: By using a single plantwide overhead rate, Harris Fabrics simplified its cost accounting process and reduced the administrative burden associated with traditional departmental allocation methods.
- Enhanced decision-making: The accurate cost allocation provided by plantwide computation enabled Harris Fabrics to make better decisions regarding product pricing, production planning, and resource allocation.
Impact on Decision-Making
The implementation of plantwide computation at Harris Fabrics had a significant impact on the company’s decision-making process. By providing more accurate product costs, the company was able to:
- Identify and prioritize profitable products:
- Adjust pricing strategies to maximize profitability:
- Optimize production schedules to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
Alternative Approaches

Harris Fabrics can consider several alternative approaches to cost allocation. Each approach has its advantages and disadvantages, which should be carefully evaluated before making a decision.
One alternative approach is to use a departmental rate. Under this approach, costs are allocated to departments based on a single rate that is calculated by dividing the total indirect costs by the total direct costs in each department. This approach is relatively simple to implement and can be used to allocate costs to departments that have similar cost structures.
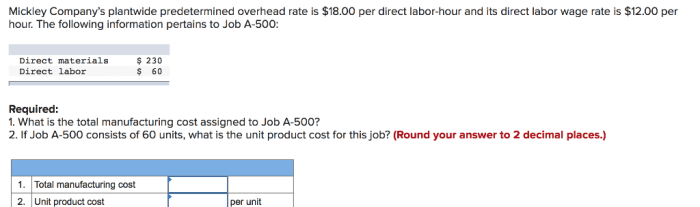
Activity-Based Costing (ABC)
Activity-based costing (ABC) is a more sophisticated approach to cost allocation that assigns costs to products and services based on the activities that are performed to produce them. This approach is more complex to implement than departmental rates, but it can provide more accurate cost information.
- Advantages of ABC:
- More accurate cost information
- Can be used to identify cost-saving opportunities
- Disadvantages of ABC:
- More complex to implement
- Requires more data collection
Best Practices and Recommendations
To ensure effective plantwide computation at Harris Fabrics, adherence to best practices and recommendations is crucial. These guidelines provide a framework for optimizing the accuracy, reliability, and usefulness of the plantwide rates.
Key considerations include:
Data Collection and Analysis
- Ensure the accuracy and completeness of data collected for plantwide computation.
- Regularly review and update data to reflect changes in operations and cost structures.
- Analyze data to identify trends, outliers, and areas for improvement in plantwide rates.
Rate Setting
- Establish clear and consistent criteria for setting plantwide rates.
- Consider both historical data and future projections when setting rates.
- Involve relevant stakeholders in the rate-setting process to ensure buy-in and understanding.
Rate Allocation
- Develop a systematic approach for allocating plantwide rates to products and services.
- Consider factors such as resource consumption, value-added, and customer profitability.
- Regularly review and adjust rate allocation methods to ensure accuracy and fairness.
Continuous Improvement, Harris fabrics computes its plantwide
- Establish a process for ongoing monitoring and evaluation of plantwide computation.
- Identify areas for improvement and implement changes to enhance accuracy and efficiency.
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement to ensure plantwide computation remains effective and relevant.
Commonly Asked Questions: Harris Fabrics Computes Its Plantwide
What is plantwide computation?
Plantwide computation is a method of allocating overhead costs across all production activities within a manufacturing facility.
What are the benefits of using plantwide computation?
Plantwide computation provides a comprehensive view of overhead costs, facilitates accurate product costing, and supports informed decision-making.
What factors influence Harris Fabrics’ plantwide overhead rates?
Factors such as production volume, labor costs, and machine utilization significantly impact Harris Fabrics’ plantwide overhead rates.