Embark on a scientific expedition with our comprehensive DNA and Replication Worksheet Answers, where we decipher the intricate mechanisms of genetic replication, unraveling the mysteries of cell division, growth, and repair.
Delve into the molecular architecture of DNA, exploring the interplay of nucleotides, base pairs, and the iconic double helix structure. Witness the remarkable process of DNA replication, guided by a symphony of enzymes, including helicase, DNA polymerase, and ligase.
DNA Structure
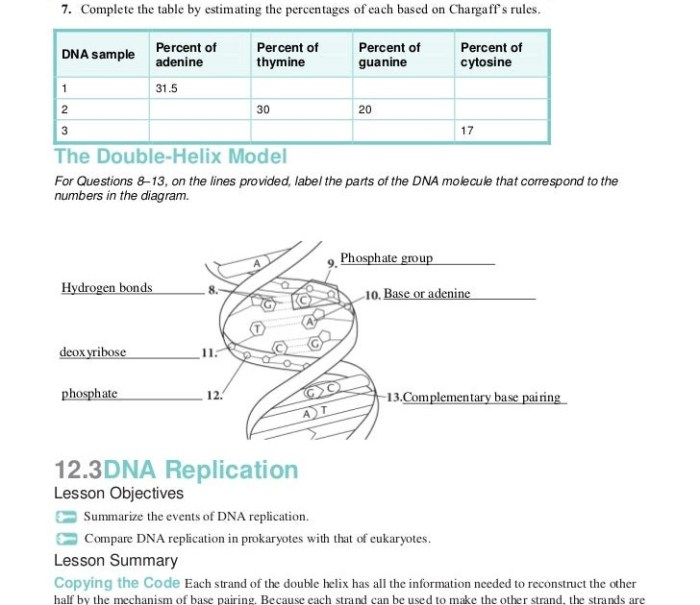
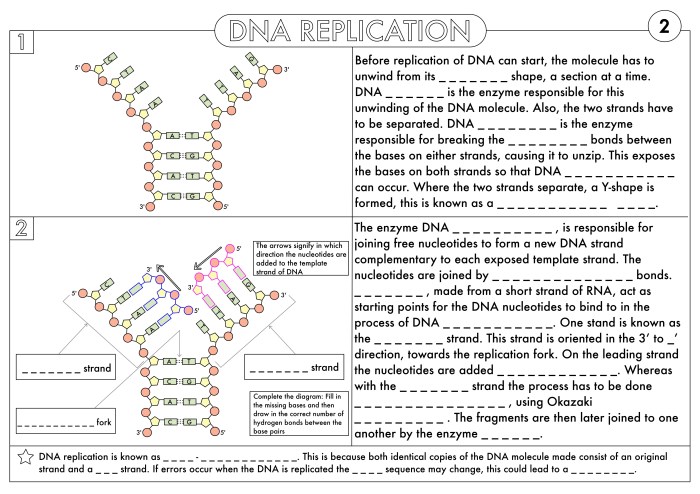
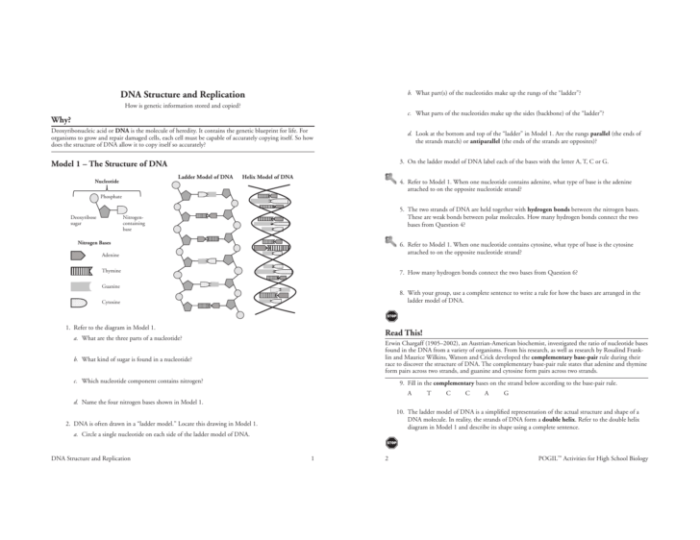
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a molecule that contains the genetic instructions for an organism. It is made up of two long strands of nucleotides that are twisted around each other to form a double helix.
Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule, a phosphate molecule, and a nitrogenous base. There are four different types of nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). The bases on the two strands of DNA are complementary, meaning that A always pairs with T, and G always pairs with C.
This complementary base pairing is what holds the two strands of DNA together.
Hydrogen Bonds
The double helix structure of DNA is maintained by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases. Hydrogen bonds are weak chemical bonds that form between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom, such as nitrogen or oxygen. In DNA, the hydrogen bonds form between the amino group of one base and the carbonyl group of another base.
DNA Replication
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes a copy of its DNA. This process is essential for cell division, growth, and repair.
Steps of DNA Replication, Dna and replication worksheet answers
DNA replication occurs in three steps: initiation, elongation, and termination.
- Initiation:Replication begins at a specific location on the DNA molecule called the origin of replication. At the origin of replication, the two strands of DNA are separated by an enzyme called helicase.
- Elongation:Once the two strands of DNA are separated, an enzyme called DNA polymerase begins to add new nucleotides to each strand. DNA polymerase adds nucleotides in a complementary fashion, meaning that an A nucleotide is added to a T nucleotide, and a G nucleotide is added to a C nucleotide.
- Termination:DNA replication continues until the entire DNA molecule has been copied. Once the DNA molecule has been copied, the two new strands of DNA are joined together by an enzyme called ligase.
Enzymes Involved in DNA Replication
Several enzymes are involved in DNA replication, including helicase, DNA polymerase, and ligase.
- Helicase:Helicase is an enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix, separating the two strands of DNA.
- DNA polymerase:DNA polymerase is an enzyme that adds new nucleotides to the growing DNA strand.
- Ligase:Ligase is an enzyme that joins the two new strands of DNA together.
Commonly Asked Questions: Dna And Replication Worksheet Answers
What are the key components of a DNA molecule?
Nucleotides, consisting of a sugar-phosphate backbone and nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine).
Describe the role of hydrogen bonds in DNA structure.
Hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs (A-T and C-G) maintain the double helix structure.
What is the significance of DNA replication?
DNA replication ensures accurate duplication of genetic material during cell division, growth, and repair.
How do enzymes contribute to DNA replication?
Helicase unwinds the double helix, DNA polymerase synthesizes new DNA strands, and ligase joins the newly synthesized fragments.
What are the potential consequences of errors in DNA replication?
Replication errors can lead to mutations and genetic disorders, affecting cellular function and potentially causing diseases.