What is the gauge pressure pgauge at point 2 – Gauge pressure, denoted as pGauge, plays a crucial role in various scientific and engineering applications. Understanding the concept of gauge pressure at point 2 is essential for accurate measurements and analysis. This comprehensive guide delves into the definition, significance, and methods for determining gauge pressure at point 2, providing a thorough understanding of this important parameter.
Point 2 in a system represents a specific location where gauge pressure is measured. The factors influencing gauge pressure at point 2 include the system’s geometry, fluid properties, and external forces. Determining gauge pressure involves utilizing pressure gauges or mathematical calculations based on the system’s characteristics.
1. Definition of Gauge Pressure (pGauge)

Gauge pressure, denoted as pGauge, measures the pressure relative to the ambient atmospheric pressure. It is commonly used in various applications, such as measuring the pressure of gases, liquids, and vapors in a system.
The mathematical formula for gauge pressure is:
pGauge = pAbsolute
pAtmospheric
where:
- pGauge is the gauge pressure
- pAbsolute is the absolute pressure
- pAtmospheric is the atmospheric pressure
Gauge pressure differs from absolute pressure in that absolute pressure measures the pressure relative to a perfect vacuum, while gauge pressure measures the pressure relative to the surrounding atmosphere.
2. Point 2 in a System
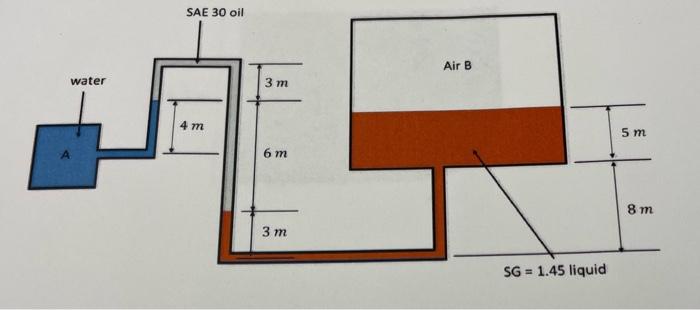
Point 2 in a system is a specific location where the gauge pressure is measured. It is typically chosen as a reference point for comparing pressure measurements within the system.
To locate point 2, consider the following factors:
- The purpose of the pressure measurement
- The location of the pressure source
- The accessibility and safety of the measurement point
The gauge pressure at point 2 can be affected by several factors, including the pressure of the surrounding atmosphere, the elevation of the measurement point, and the temperature of the fluid.
3. Determining Gauge Pressure at Point 2
To determine the gauge pressure at point 2, the following steps can be taken:
- Measure the absolute pressure at point 2 using a pressure gauge.
- Measure the atmospheric pressure using a barometer or other suitable instrument.
- Calculate the gauge pressure using the formula: pGauge = pAbsolute
pAtmospheric.
Pressure gauges are commonly used to measure gauge pressure. They come in various types, including mechanical, electrical, and digital gauges.
4. Applications of Gauge Pressure

Gauge pressure has numerous practical applications in various industries and technologies:
- Monitoring pressure in pipelines and tanks
- Controlling fluid flow in hydraulic and pneumatic systems
- Measuring the altitude of aircraft
- Calibrating pressure sensors and instruments
In everyday life, gauge pressure is used in devices such as tire gauges, blood pressure monitors, and depth gauges.
Answers to Common Questions: What Is The Gauge Pressure Pgauge At Point 2
What is the difference between gauge pressure and absolute pressure?
Gauge pressure measures the pressure relative to atmospheric pressure, while absolute pressure measures the pressure relative to a perfect vacuum.
How do I calculate gauge pressure at point 2?
Gauge pressure at point 2 can be calculated using a pressure gauge or by subtracting atmospheric pressure from absolute pressure.
What are the factors that affect gauge pressure at point 2?
Factors affecting gauge pressure at point 2 include fluid density, height of the fluid column, and external forces.