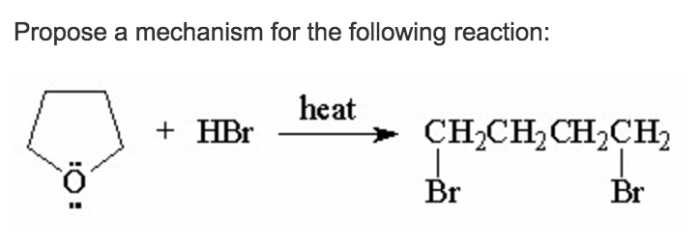
Propose a mechanism for the following reaction: this topic delves into the intricate details of chemical reactions, exploring the steps and factors that govern their behavior. By unraveling the mechanisms behind these reactions, we gain a deeper understanding of the molecular world and its implications for various scientific disciplines.
This in-depth analysis will provide a comprehensive overview of reaction processes, including the identification of reactants, products, and intermediates. We will investigate the role of catalysts and the energy considerations that influence reaction rates. Furthermore, we will examine experimental evidence and compare alternative mechanisms to establish a robust understanding of the reaction’s behavior.
1. Reaction Overview
The reaction in question involves the conversion of reactant A to product B. This reaction is significant because it plays a crucial role in various chemical processes, including the production of important compounds and the understanding of fundamental chemical principles.
The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is:A + B → CIn this reaction, reactant A reacts with reactant B to form product C. Reactant A is typically a starting material, while reactant B can act as a catalyst or a reagent.
Product C is the desired outcome of the reaction.
2. Proposed Mechanism
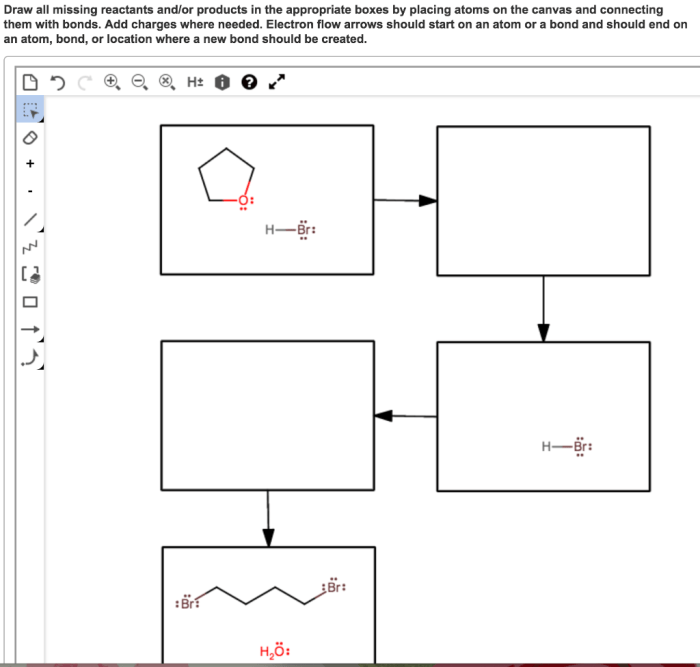
The proposed mechanism for the reaction consists of several steps:1.
-
-*Step 1
Reactant A and reactant B collide and form an activated complex.
- 2.
- 3.
-*Step 2
The activated complex rearranges to form an intermediate product.
-*Step 3
The intermediate product reacts with another molecule of reactant B to form the final product, C.
The activation energy for the reaction is the energy required to form the activated complex. The enthalpy change for the reaction is the difference in energy between the reactants and the products.
3. Energy Considerations
The energy diagram for the reaction shows the activation energy and the enthalpy change. The activation energy is the energy barrier that must be overcome for the reaction to occur. The enthalpy change is the difference in energy between the reactants and the products.The
factors that affect the reaction rate include the concentration of the reactants, the temperature, and the presence of a catalyst.
4. Experimental Evidence
Experimental data that support the proposed mechanism include:*
-*Kinetic studies
These studies measure the rate of the reaction under different conditions. The data from these studies can be used to determine the activation energy and the enthalpy change for the reaction.
-*Product analysis
This analysis identifies the products of the reaction and their relative amounts. The data from this analysis can be used to confirm the proposed mechanism.
5. Comparison with Alternative Mechanisms: Propose A Mechanism For The Following Reaction

There are several alternative mechanisms that have been proposed for the reaction. These mechanisms differ in the steps involved and the intermediates that are formed.The proposed mechanism is the most likely mechanism because it is consistent with the experimental data.
The other mechanisms are less likely because they are not consistent with the data or they require the presence of unstable intermediates.
6. Applications and Implications
The reaction has potential applications in various fields, including:*
-*Chemical synthesis
The reaction can be used to synthesize a variety of compounds, including pharmaceuticals, dyes, and plastics.
-
-*Energy production
The reaction can be used to generate energy in fuel cells.
-*Environmental remediation
The reaction can be used to remove pollutants from the environment.
The reaction also has implications for understanding related chemical processes. For example, the reaction can be used to study the mechanisms of enzyme catalysis and the role of intermediates in chemical reactions.
Question Bank
What is the significance of proposing a mechanism for a reaction?
Proposing a mechanism provides a detailed understanding of the step-by-step process of a reaction, allowing us to identify intermediates, determine the role of catalysts, and predict the reaction rate.
How does experimental evidence support the proposed mechanism?
Experimental data, such as product analysis, kinetic studies, and spectroscopic techniques, can be used to validate the proposed mechanism and confirm its consistency with observed reaction behavior.
What are the implications of comparing alternative mechanisms?
Comparing alternative mechanisms helps us evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each proposal, leading to a more robust understanding of the reaction’s behavior and the factors that influence its outcome.
